Neurosurgery is a broad term used to describe surgical procedures performed on the spinal column, brain and spinal cord. These procedures are performed to treat a wide range of injuries and illnesses, from brain cancer to epilepsy. Keep reading to learn more about this medical specialty and how it can help improve function and even save lives.
Types of Neurosurgery
Even though the nervous system only has a few main components, it's extremely complex. Nerves use electrical signals to control many of the body's most important functions, including digestion, movement, breathing and memory. Because the nervous system is so complex, neurosurgery has several subspecialties that focus on treating specific body parts or medical conditions.
General Neurosurgery
General surgeons treat a wide range of conditions, including tethered spinal cord, slipped discs and spinal stenosis. Before performing surgery, a general neurosurgeon may order a wide range of imaging studies and procedures to determine the extent of the problem and develop an appropriate treatment plan. These procedures include biopsies, electroencephalograms (EEGs), myelograms and angiograms.
Spinal Neurosurgery
Spine disorders and spinal injuries can have a serious impact on your life. Because the spine acts as a support structure for your body, spinal problems interfere with walking, standing, bending and lifting. In serious cases, spine disorders even make it difficult to earn a living, especially for people whose jobs require heavy lifting or frequent standing. Spinal neurosurgery is used to treat these problems, improving function and making it easier to do everything from hold a baby to carry a load of groceries.
Spinal neurosurgery may be used to treat the following:
- Scoliosis: Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature of the spine. If braces don't work, surgery may be used to prevent the condition from getting worse. Spinal fusion and vertebral body tethering are two procedures used to help people with scoliosis. During a spinal fusion procedure, a surgeon connects some of the bones in the spine so that they can't move around. Vertebral body tethering involves the placement of small screws along the abnormal curve. Once the screws are in place, a surgeon threads a flexible cord through them. Tightening the cord helps the spine straighten.
- Disk herniation: Your spine is made up of small bones called vertebrae. In between the vertebrae are flat, round structures known as intervertebral disks. These disks are responsible for absorbing shock when you're walking or running. Each disk has a soft center and a hard exterior. A disk herniates when the soft center starts to push against the hard outer ring. During a microdiscectomy, a neurosurgeon removes the herniated part of the disk, relieving pressure on the spinal nerve.
- Degenerative disk disease: Herniation isn't the only problem that affects the intervertebral disks. As you age, your disks lose water, making them less effective at shock absorption. Injuries and high-impact activities can also cause the disks to tear. When degenerative disk disease develops, it typically causes pain that is worse when sitting than standing or walking. It can also cause foot drop, leg weakness or numbness and tingling. This condition is often treated with artificial disk replacement or spinal fusion.
- Spinal stenosis: The spine contains open spaces to ensure there's enough room for the spinal cord and spinal nerves. In some people, these spaces get narrower, putting pressure on the nerves and causing pain, numbness, tingling and other symptoms. This is known as spinal stenosis. Surgery typically isn't performed unless noninvasive treatment options, such as medications and physical therapy, don't work. If surgery is necessary, a neurosurgeon may perform a laminectomy, laminoplasty or laminotomy. Minimally invasive surgery may also be an option.
- Spinal tumors: Neurosurgical procedures are also used to remove benign and malignant tumors from the spine.
Cerebrovascular Neurosurgery
Cerebrovascular neurosurgery focuses on arteriovenous malformations, stroke and aneurysms. An arteriovenous malformation occurs when a group of blood vessels get tangled, preventing blood from flowing normally. When an AVM forms in the brain, it can prevent the brain from getting enough oxygen, resulting in seizures, headaches or muscle weakness. A neurosurgeon may treat a brain AVM by performing radiosurgery, endovascular embolization or surgical resection.
Some of the blood vessels in your body are responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood to your brain. A stroke occurs when one of these vessels ruptures or is blocked by a blood clot, restricting normal blood flow. In some cases, a stroke is treated with a procedure called carotid endarterectomy. During this procedure, a doctor removes plaque from the wall of the affected artery. Plaque is a waxy substance made from calcium, fat and cholesterol.
A brain aneurysm is a weakening of one of the blood vessels in the brain. Initially, an aneurysm may produce no symptoms, but it can quickly turn life-threatening if it bursts. A brain aneurysm may also cause pain, dilated pupils, double vision and other symptoms if it presses on the nerves in the brain. Depending on the size and location of the aneurysm, a neurosurgeon may decide to clip it or perform an endovascular procedure, which is less invasive.
Neuro-oncology

Neuro-oncology is a subspecialty dedicated to helping people with cancers of the brain and other parts of the nervous system. For many people, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are successful at shrinking tumors and alleviating the pain, vision changes and other symptoms that can occur with this type of cancer. If other treatments don't work, surgery to remove the tumor may be an option. Neurosurgeons base the decision to perform surgery on several factors, such as the age of the patient, the type of tumor the patient has and whether the patient has any serious risk factors.
Is Neurosurgery Always Necessary?
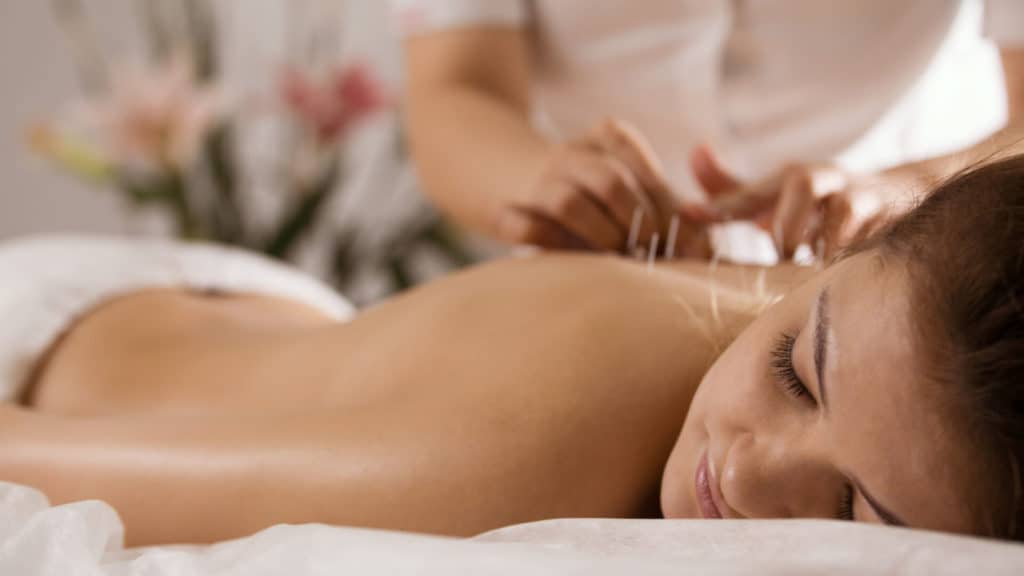

Although diseases and injuries to the nervous system can cause pain and other symptoms, surgery isn't always the answer. At Northeast Spine and Sports Medicine, we offer a wide range of nonsurgical treatments, including acupuncture, chiropractic care, physical therapy and pain management. If surgery is necessary, we'll discuss each option with you in detail and make sure you have all the information you need to make decisions about your care. To learn more about our multidisciplinary approach to patient care, call (732) 653-1000.


