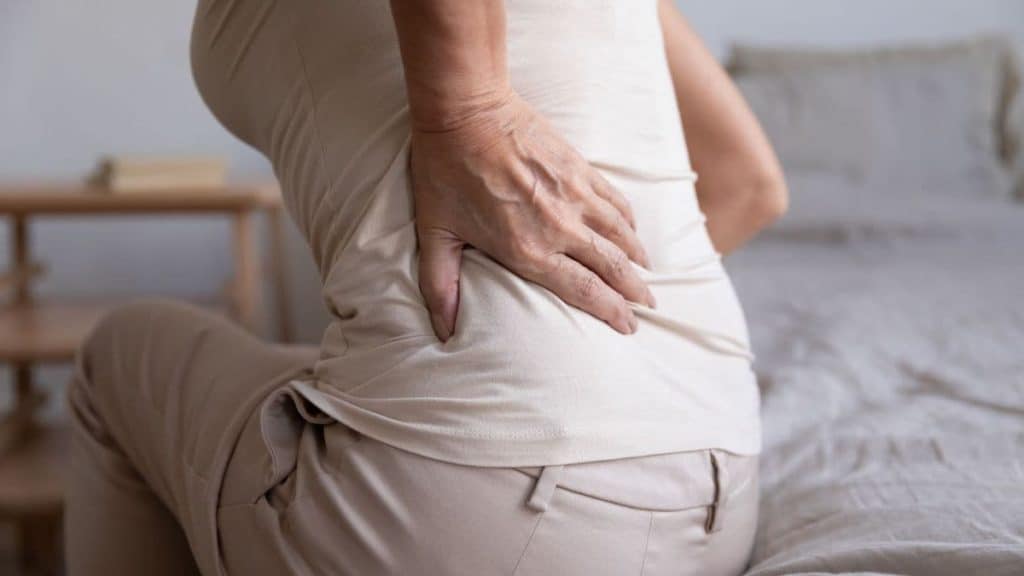
Musculoskeletal disorders, many of which cause chronic back pain, are one of the leading causes of disability in the United States. Because the back is involved in walking, bending and other activities, chronic back pain makes it difficult to perform routine tasks and may even cause muscle weakness and prevent you from getting a restful night's sleep.
If over-the-counter pain relievers and muscle relaxants aren't giving you much relief, it's time to seek professional care from a healthcare provider. Although surgery is helpful for many people, it's also invasive and expensive. It may take months to recover completely, making it difficult to work, attend school or enjoy your favorite hobbies. That's why nonsurgical back pain treatment should be the first thing you try. If you have chronic back pain, you may benefit from any of the following treatments.
5 Nonsurgical Treatment Options
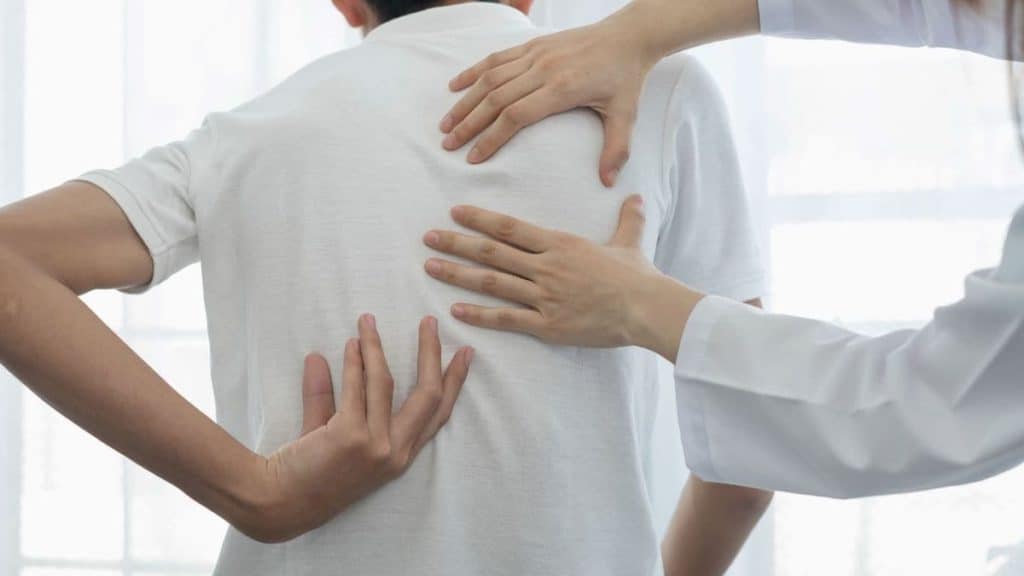
Many professional medical services provide back pain relief without the need for surgery so you can return to your daily activities. Depending on the cause and severity level of your back pain, your care team may recommend some of the following nonsurgical back pain treatment methods.
1. Physical Therapy
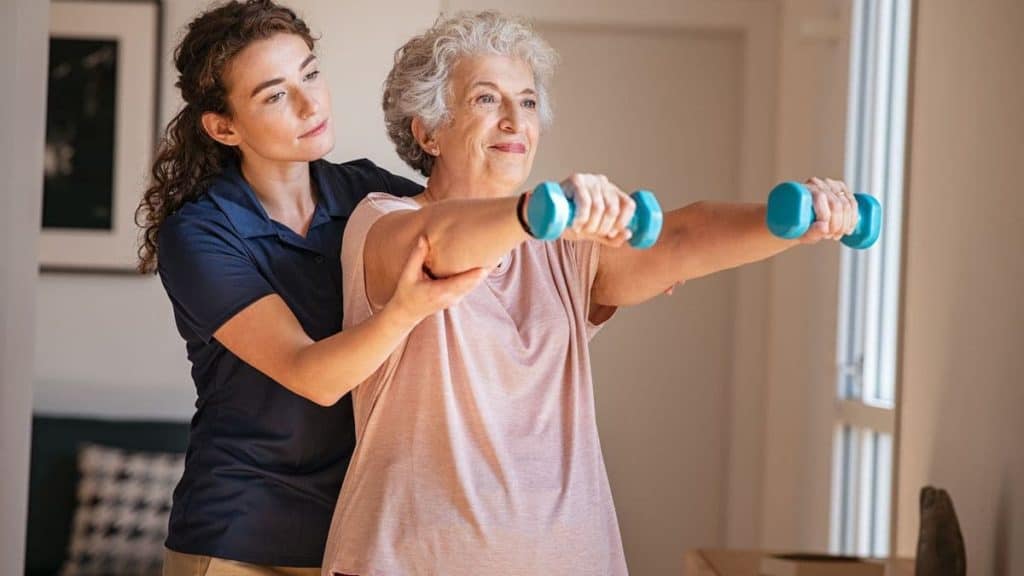

Physical therapy for back pain stretches tight muscles, increases flexibility and improves your range of motion, making it one of the most common nonsurgical treatments for relieving severe pain. Professional physical therapists often use their hands to stretch, massage or manipulate the muscles, addressing many of the most common causes of discomfort in the upper and lower back. During a physical therapy session, a physical therapist may also show you how to perform specific exercises to strengthen your muscles, prevent back pain from recurring, and provide other long-term benefits.
2. Spinal Manipulation and Decompression
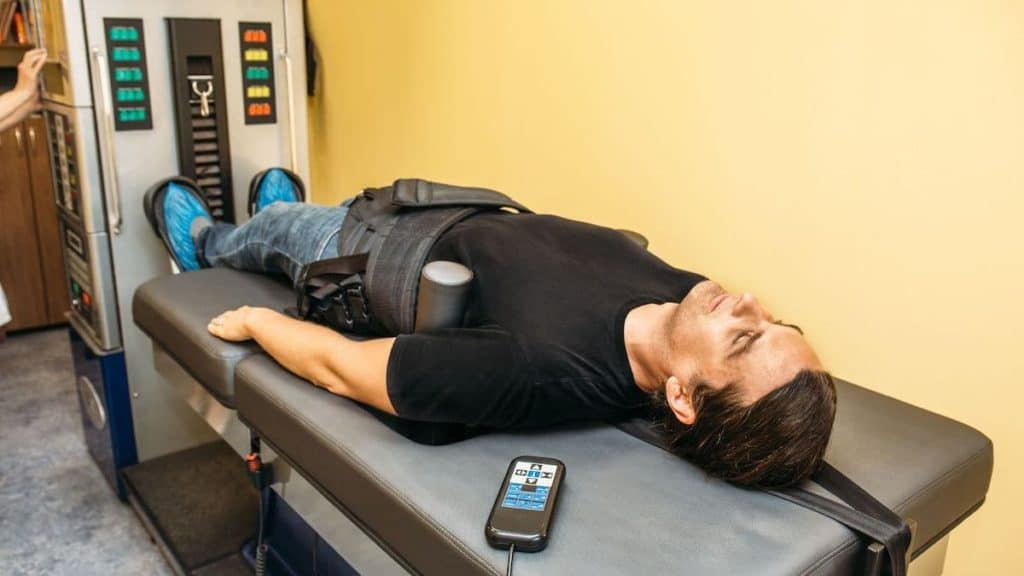
Spinal manipulation and decompression are some of the most common types of chiropractic care available. Physical therapists and osteopathic physicians also use spinal manipulation in their physical exam practices. Spinal manipulation, commonly referred to as spinal adjustment, involves using the hands or a special device to realign the bones in the spine. If your back pain is a result of misalignment, spinal manipulation can bring you much-needed relief.
Spinal decompression eases back pain by reducing the amount of pressure on the joints and discs in the spine. During a decompression session, motorized traction gently stretches and pulls your spine, moving the discs back into their normal position. If your back pain is the result of a herniated disc or bulging disc, this nonsurgical treatment may help you see an improvement in pain.
3. Acupuncture
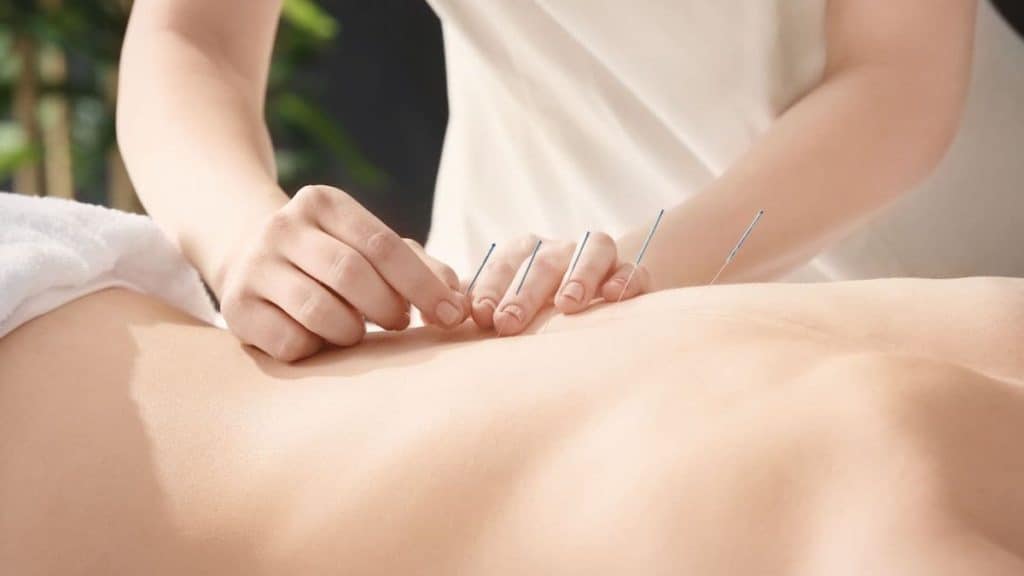
Acupuncture for back pain is another common nonsurgical treatment option. During an acupuncture session, an experienced practitioner inserts thin needles at certain points on your body, restoring the normal flow of energy. According to researchers from Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute, acupuncture works just as well for the management of pain as other forms of treatment.
Acupuncture is also a low-risk option for treating back pain. Although you may feel some tingling at the insertion site, it shouldn't cause any discomfort or other side effects. Needles stimulate the release of endorphins, dopamine, serotonin and other chemicals that help manage pain. Acupuncture may also increase blood flow around the spinal nerve, reducing pain and helping damaged tissue heal faster.
4. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
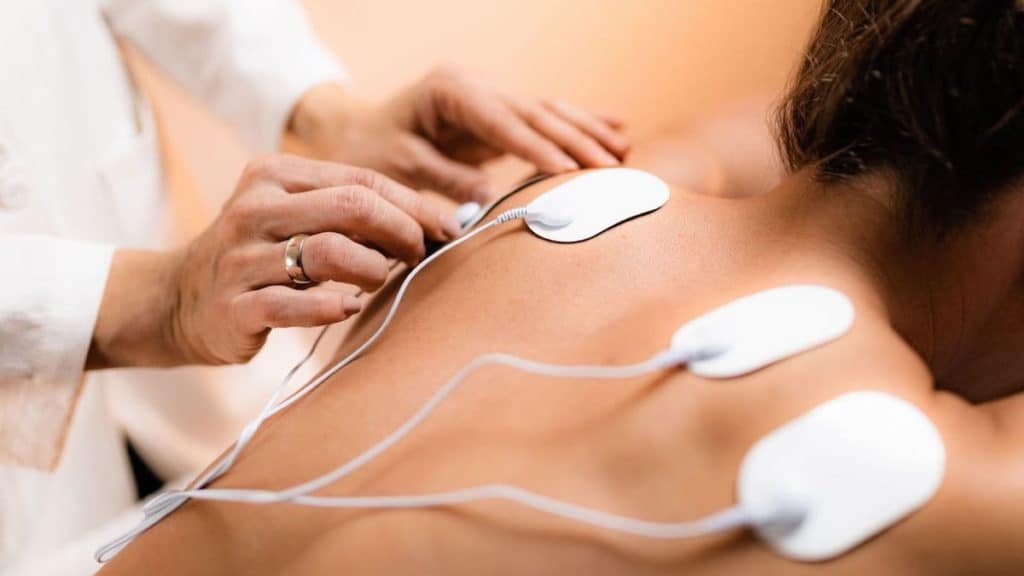
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) uses small electrical pulses to interrupt the transmission of pain signals to the brain. Electrical pulses also relax the muscles and stimulate the release of endorphins, the same chemicals that make you feel good when you exercise.
Several companies produce TENS devices for home use, but it's best to ask your care team after or during a physical exam if TENS is appropriate for your condition. Although TENS helps relieve back pain, it isn't right for everyone. For example, if you have a spinal cord stimulator, pacemaker or other implanted device, clinical guidelines say you won't be able to try TENS because the electrical pulses may interfere with it.
5. Heat Therapy
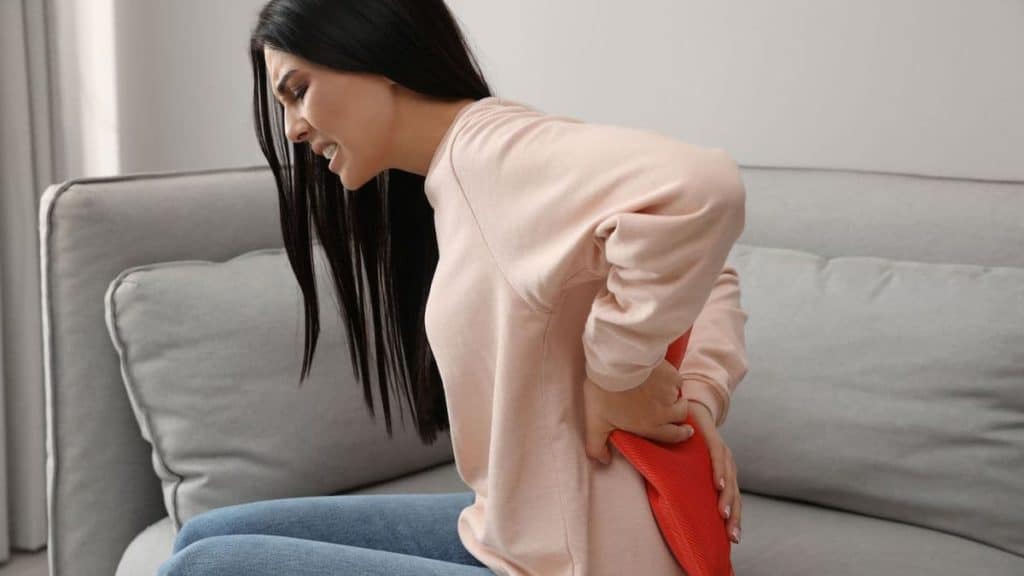

For chronic back pain, heat therapy works better than cold therapy. Although cold therapy relieves pain, it does so by restricting blood flow. This makes it more suitable for acute injuries. In contrast, heat therapy increases blood flow and improves circulation, making it ideal for chronic back pain. Your care team may recommend one or more of the following:
- Soaking in a tub of hot water
- Using topical treatments containing capsaicin
- Applying a hot water bottle or heating pad to the painful areas of your back
Heat helps relieve pain, but it's not always an appropriate treatment. You shouldn't apply heat to your sore back if the affected area is numb, if you have an open wound or if the skin on your back is inflamed. If you have heart disease or high blood pressure, check with your care team before using heat therapy to relieve chronic back pain.
6 Self-Management Tips for Back Pain Relief

In addition to nonsurgical back pain treatment options, these lifestyle changes may reduce your pain and help you regain function without the need for prescription drugs or surgery.
1. Stay Mobile

If your pain is due to a pulled muscle or another type of acute injury, your care team may advise you to rest while it heals. For chronic back pain, however, scientific evidence suggests it's important to move as much as you can. A sedentary lifestyle causes the muscles in the back to become deconditioned, making them weaker and less capable of supporting your body as you work and do all the things you enjoy. Once those muscles weaken, it becomes more difficult to exercise regularly, making the pain even worse.
If your care team says it's okay to exercise, consider getting a membership at your local swimming pool. For many people, cool water feels good on sore back muscles. Swimming is an exercise therapy that’s also easier on the joints than jogging and other types of exercise. Additional benefits include pain relief, improved circulation and less muscle stiffness. If the pool isn't for you, try walking and light stretching until your care team gives you the go-ahead for more strenuous activities.
2. Relieve Stress

You're probably aware that high levels of stress aren't good for your mental well-being. What you may not know is that stress also contributes to muscle pain. This is because your body responds to stress by tightening your muscles. As soon as the stressful situation ends, your muscles return to normal. For people with chronic stress, however, the body never has a chance to truly relax, leading to long-term pain and other symptoms.
Stress comes in many forms, from completing a big project at work to worrying about an aging parent or sick child. If you're currently going through a stressful situation, try at least one of the following forms of stress relief and psychological therapy:
- Massage: Massage triggers the release of hormones that help you relax and feel better. As an added bonus, massage is one of the techniques that many physical therapists use on people with chronic back pain, so it may also provide pain relief.
- Yoga: When you do yoga, you stretch your muscles and focus on your breathing. This relieves psychological tension and may help reduce your back pain.
- Socializing: Laughing and sharing stories with other people can help you shed some of the stress you've been feeling, allowing your body to relax instead of keeping your muscles tight.
- Meditation: During a meditation session, you focus on an intention and clear other thoughts from your mind. Therefore, meditation helps you relax and focus on something other than the stress in your life.
- Sleep: If you've been "burning the candle at both ends," adopting better sleep habits may help. Adults need at least 7 hours of sleep each night, and you may need more if you maintain an active lifestyle. Getting the right amount of sleep improves your mood and may make it easier to handle stressful situations as they arise.
3. Consider Weight Loss

Excess weight causes the discs in your spine to wear out faster than they should, leading to chronic back pain. Spinal discs are rubbery pads that cushion your vertebrae against shock. Extra weight and obesity also put extra stress on the joints and muscles, which may make the pain in your back worse or cause pain in other parts of your body. Losing weight reduces this stress, easing pain and improving your physical functioning.
It's important to consult with your care team before embarking on a weight-loss journey, as you may need to do modified exercises or follow a special diet plan if you have any chronic conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease or heart disease. If your doctor or another health professional clears you, start off slowly and make small changes along the way. Here are a few things to try.
- Instead of eating white bread and other foods made with refined grains, look for products with whole grains.
- Watch your intake of added sugars, which are found in cookies, candy, soft drinks, processed meats, condiments and many other foods.
- Eat lean meats and poultry instead of fatty cuts of meat.
- Increase your intake of fruits and vegetables.
- Do as much physical activity as you can tolerate.
When it comes to weight loss, slow and steady wins the race, so don't get discouraged if you don't lose weight quickly. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, you should aim for 1-2 pounds per week.
4. Wear Proper Footwear

Even though you wear shoes on your feet, choosing the wrong footwear can cause chronic back pain. This is because certain shoes can cause your hips, spine and legs to go out of alignment, putting extra stress on your lower back. Some shoes also make it difficult to maintain good posture, making your back pain even worse.
If you typically wear high heels, try switching to flats. High heels place your feet at an unnatural angle, affecting the plantar fascia, calf muscles and hamstrings. Your hamstrings are connected to your lower back, so it's no surprise that wearing heels is associated with back pain. Whether you need dress shoes or athletic shoes, look for a pair that offers plenty of support and cushioning.
5. Maintain an Anti-Inflammatory Diet

Chronic pain sometimes occurs due to high levels of inflammation. If this is the cause of your back pain, following an anti-inflammatory diet may help. An anti-inflammatory diet limits the consumption of pro-inflammatory foods and encourages the consumption of foods that fight inflammation.
Foods that promote inflammation include refined carbohydrates, soft drinks, red meat, fried foods, margarine and other processed foods. Tomatoes, nuts, olive oil, fatty fish, fruits and green, leafy vegetables help fight inflammation. Here are a few ways to work these anti-inflammatory foods into your diet.
- Blend your favorite fruits with spinach to create a nutrient-packed smoothie.
- Add tomato slices to your sandwiches or eat a few grape tomatoes as a snack.
- Cook with olive oil instead of other types of oil when possible.
- Eat salads made with spinach, kale and other leafy greens.
- Snack on walnuts, almonds or other nuts. Just be careful not to eat too many nuts at one time, as they're high in calories.
- Try eating swordfish or tuna for dinner at least one night per week.
6. Reposition How You Sleep

Additional studies prove that your sleeping position has a major impact on the alignment of your spine. As a result, the way you sleep could be contributing to your chronic back pain. Keck Medicine of USC recommends sleeping on your back with one pillow under your head and another pillow behind your knees, with one caveat. You shouldn't use this sleep position if you're pregnant, as it can affect circulation to the developing baby.
If you can't sleep on your back due to pregnancy or just don't feel comfortable sleeping on your back, try sleeping on your side with your legs straight. Putting a pillow between your knees can keep everything aligned correctly, preventing back pain in the morning. Bending your knees isn't recommended because it can put stress on your joints. Try to avoid sleeping on your stomach, as it flattens the curve of the spine, putting extra stress on your joints and muscles.
How to Know When You Need Surgery

Non Surgical back pain treatment works for many people, but it's not always the answer. If lifestyle changes and nonsurgical medical treatments aren't bringing you the relief you need, talk to your healthcare provider about your surgical options. Only an experienced professional can determine if surgery is necessary and likely to relieve your pain.
Start Your Journey Toward Drug-Free Pain Relief

At Northeast Spine and Sports Medicine, we use an interdisciplinary approach to pain management. Sports medicine specialists, physical therapists, chiropractic professionals and other experts are available to identify the source of your pain and provide appropriate medical treatments.
We also have a pain management clinic staffed by compassionate healthcare providers. If chronic back pain is interfering with your life, book an appointment online or call us at (732) 653-1000.


